Understanding Autonomous Vehicle Technology
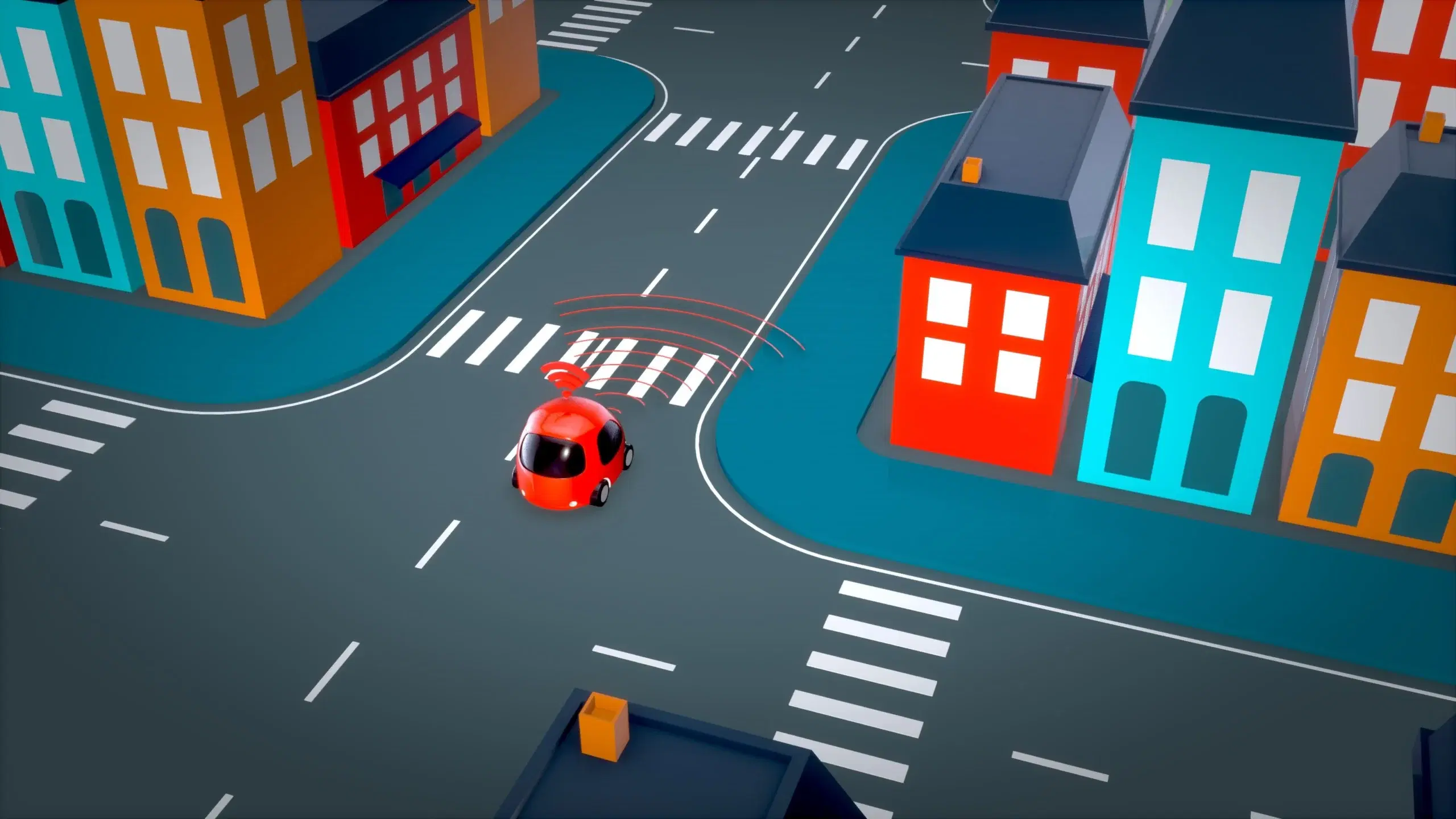


An Autonomous vehicle uses advanced sensors, cameras, mapping technology, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to navigate roads and operates without human intervention. This article explains the six levels of automation in autonomous vehicles, with Level 0 requiring the driver to perform all tasks and Level 5 operating without human input. It also explains that autonomous vehicles are expected to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and provide accessibility for people with disabilities, challenges remain, including legal and regulatory issues, cybersecurity concerns, and public acceptance. We will also see how ongoing advancements in sensor technology, machine learning, and communication systems will continue to shape the development of autonomous vehicle technology.

What is an Autonomous Vehicle?
An autonomous vehicle, also known as a self-driving car, is a vehicle that can navigate and operate on the road without the need for human intervention. These vehicles are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to perceive their surroundings and respond to traffic conditions in real-time. The combination of these technologies, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms allows autonomous vehicles to make complex decisions and control the vehicle’s movements.
Autonomous vehicles are classified into six levels of automation, ranging from no automation (Level 0) to full automation (Level 5). Level 0 vehicles require the driver to perform all driving tasks, while Level 5 vehicles can operate in any driving condition without human input. The development of autonomous vehicles is set to revolutionize the transportation industry by improving safety, reducing traffic congestion, and providing greater accessibility to transportation for people with disabilities or limited mobility.
However, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles faces several challenges, including legal and regulatory issues, cybersecurity concerns, and public acceptance and trust. Despite these challenges, many companies are investing heavily in developing and testing autonomous vehicle technology, and the future of transportation looks increasingly autonomous.
The Technology Behind Autonomous Vehicle
The technology behind autonomous vehicles is complex and involves a combination of advanced sensors, cameras, mapping, and communication technology. These vehicles use a variety of sensors such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and cameras to perceive their surroundings and collect data about the road, traffic, and other objects. LiDAR sensors use laser light to create a detailed 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings, while radar sensors use radio waves to detect objects and determine their distance and speed.
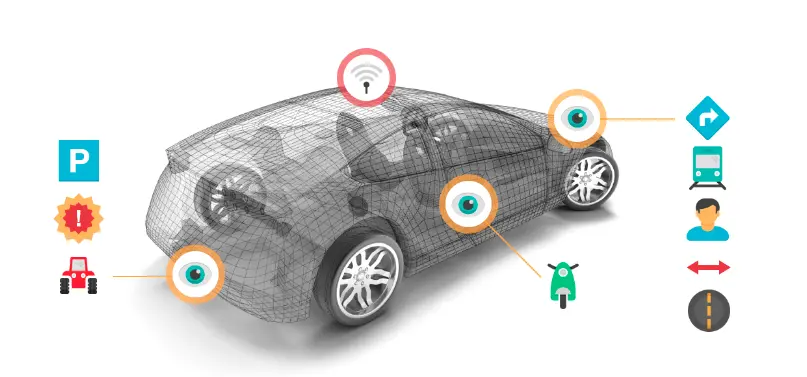
In addition to sensing technology, autonomous vehicles rely on mapping and localization technology to determine their precise location and route plans. This involves using high-precision GPS and machine-learning algorithms that analyze data from various sensors and sources to create a detailed map of the environment.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also critical components of autonomous vehicle technology, allowing the vehicle to interpret sensor data and decide how to respond to traffic and other objects on the road. Communication technology enables autonomous vehicles to communicate with each other and other infrastructure, such as traffic lights and road signs.
The technology behind autonomous vehicles is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements in areas such as sensor technology, machine learning, and communication systems, paving the way for a future where self-driving cars will be commonplace transportation.
Levels of Autonomous Vehicle
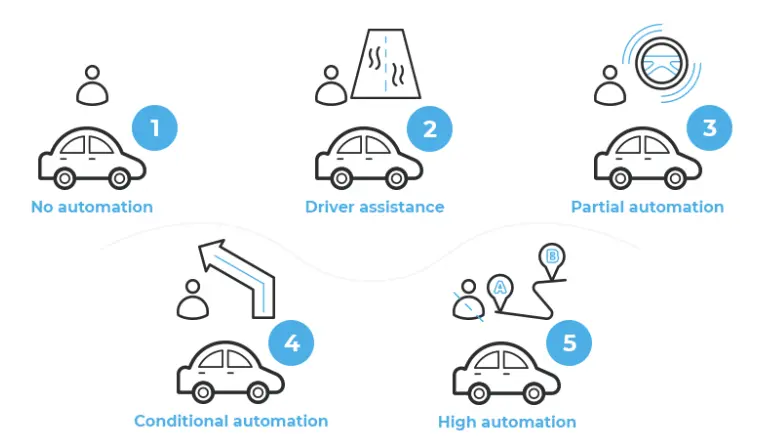
Autonomous vehicles are classified into several levels of automation, each with increasing levels of autonomy. These levels indicate the extent to which the vehicle can operate without human intervention, with the highest level allowing for fully automated driving.
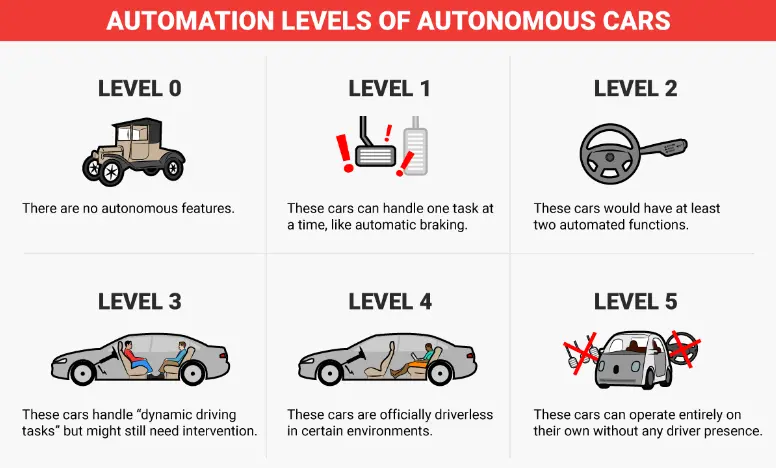
Level 0: No Automation
Level 0 is the lowest level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the driver is solely responsible for all driving tasks. In Level 0 vehicles, there are no automated driving features, and the driver must constantly monitor the road, control the vehicle’s speed, and make decisions regarding acceleration and braking. This level of automation is present in traditional vehicles without advanced driver assistance systems. While Level 0 vehicles do not have any automated features, they may still incorporate safety features such as anti-lock brakes and electronic stability control. However, Level 0 vehicles have some limitations to enhance safety and reduce the workload of the driver, as they require constant manual input and attention from the driver.
Level 1: Driver Assistance
Level 1 is the first level of automation in autonomous vehicles. These vehicles feature basic driver assistance systems. In Level 1 vehicles, the driver controls the steering, acceleration, and braking, but the vehicle can assist in these tasks. Common examples of Level 1 features include adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automated emergency braking. These features use sensors and cameras to detect other vehicles and objects on the road and can provide warnings or intervene to prevent collisions. While Level 1 vehicles provide some assistance to the driver, they still require constant monitoring and control by the driver.
Level 2: Partial Automation
Level 2 is the second level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle can provide more advanced assistance to the driver. In Level 2 vehicles, the vehicle can control both steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver must still remain vigilant and be ready to take control at any time.
Common examples of Level 2 features include Tesla’s Autopilot and General Motor’s Super Cruise, which use a combination of sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to provide advanced driver assistance features such as lane keeping, automated lane changing, and self-parking. However, the driver must still be aware of their surroundings and ready to take over control if necessary. These vehicles represent a significant step towards fully autonomous vehicles, but there are still limitations to the level of autonomy without full control by the vehicle.
Level 3: Conditional Automation
Level 3 is the third level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle is capable of taking full control under certain conditions. In Level 3 vehicles, the driver can relinquish control of the vehicle and allow it to operate autonomously in specific situations, such as on the highway or in traffic jams. However, the driver must still be prepared to take control when prompted by the vehicle.
Level 3 vehicles use advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to perceive their surroundings and decide how to navigate the road. These vehicles can detect traffic lights, road signs, and other road objects and adjust their speed and direction accordingly. However, the driver must remain alert and ready to take control if the vehicle encounters a situation it cannot handle.
Level 3 vehicles offer a higher level of autonomy than Level 2 vehicles. However, there are still limitations to their capabilities, and the driver must be prepared to take control if necessary. The development of Level 3 vehicles is an important step towards fully autonomous vehicles, but there are still challenges to overcome before this level of automation becomes mainstream.
Level 4: High Automation
Level 4 is the fourth level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle can be fully autonomous in certain conditions and environments. In Level 4 vehicles, the vehicle can operate without human intervention in specific situations, such as on highways or in predefined geofenced areas.
Level 4 vehicles use advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to detect and interpret their surroundings and can make decisions about navigating the road without any human input. These vehicles can adjust their speed, direction, and response to traffic signals and road conditions and safely navigate most environments without human intervention.
Level 4 vehicles represent a significant milestone in developing autonomous vehicles, as they offer a high level of autonomy without requiring constant human supervision. However, there are still limitations to their capabilities, and the driver may need to take control in certain situations, such as extreme weather conditions or unexpected obstacles on the road. These vehicles significantly improve safety and convenience over traditional vehicles and are a major step towards fully autonomous vehicles.
Level 5: Full Automation
Level 5 is the highest level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle can be fully autonomous in all conditions and environments without requiring human intervention. In Level 5 vehicles, the driver is completely free from the driving task. The vehicle can operate independently in any situation, including extreme weather conditions and unexpected obstacles on the road.
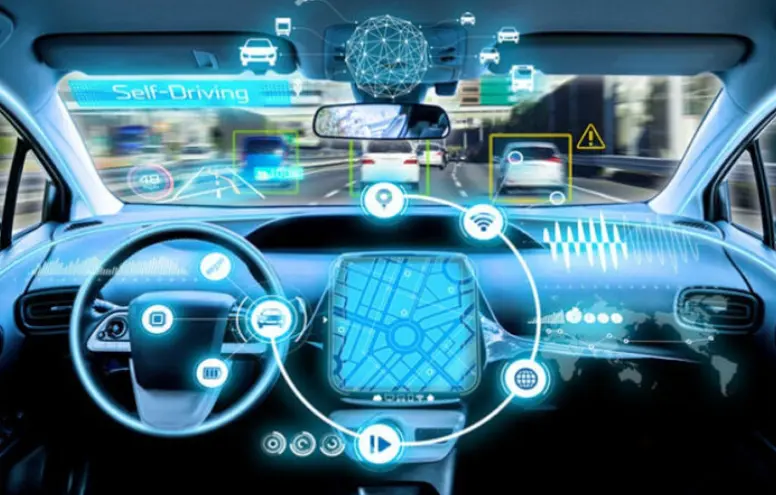

Level 5 vehicles use a combination of advanced sensors, cameras, mapping technology, and artificial intelligence to perceive their surroundings and make decisions about how to navigate the road. These vehicles can adjust their speed, direction, and response to traffic signals and road conditions and safely navigate any environment without human input.
Full automation offers a significant improvement in safety, efficiency, and convenience over traditional vehicles and has the potential to transform transportation as we know it. However, the development and deployment of Level 5 vehicles are still in the early stages. Significant technical, legal, and societal challenges are present before they become a reality.
Applications of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles have a wide range of potential applications across different industries and sectors. Some of the most promising applications of autonomous vehicles include:
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles can provide an efficient and safe mode of transportation for people and goods. They can be used for public transportation, ride-sharing, delivery services, and more.
- Logistics and supply chain: Autonomous vehicles can improve the efficiency and accuracy of logistics and supply chain operations by automating the movement of goods and reducing the need for manual labor.
- Agriculture: Autonomous vehicles can be used in agriculture to automate tasks such as planting, watering, and harvesting crops, improving efficiency and reducing the need for manual labor.
- Mining: Autonomous vehicles can be used in mining operations to automate the movement of materials and reduce the risk of accidents in hazardous environments.
- Construction: Autonomous vehicles can be used in construction to automate tasks such as excavation, demolition, and transportation of materials, improving safety and efficiency.
- Military: Autonomous vehicles can be used in military operations to support reconnaissance, surveillance, and logistics, reducing the risk to human personnel.
- Emergency services: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to use in emergency services to transport people and supplies to disaster areas or provide remote medical assistance.

Autonomous vehicles have the potential to revolutionize various industries and improve safety, efficiency, and sustainability. However, their widespread adoption depends on overcoming technical, legal, and societal challenges, such as ensuring safety, addressing ethical concerns, and integrating them with existing infrastructure and systems.
Advantages of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles have numerous advantages over traditional vehicles, which make them an attractive technology for future transportation systems. Some of the main advantages of autonomous vehicles are:
- Increased safety: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to greatly reduce the number of accidents caused by human error, which is estimated to be the cause of over 90% of all accidents. By using advanced sensors and algorithms, autonomous vehicles can detect and avoid obstacles and hazards in the environment. It makes them safer than human-driven vehicles.
- Improved traffic flow: Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other and the surrounding infrastructure to optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and travel times.
- Increased efficiency: Autonomous vehicles can operate more efficiently than human-driven vehicles by reducing unnecessary acceleration and braking and optimizing routes based on real-time traffic conditions.
- Improved accessibility: Autonomous vehicles can provide greater mobility for people who are unable to drive, such as the elderly and disabled, improving their independence and quality of life.
- Reduced environmental impact: Autonomous vehicles can be designed to operate on electric power, reducing their emissions and contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
- Lower operating costs: Autonomous vehicles can reduce the cost of transportation by reducing the need for human drivers and optimizing maintenance schedules.
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to improve safety, efficiency, accessibility, and sustainability in transportation. However, their widespread adoption will require significant investments in research and development, infrastructure, and public acceptance.
Challenges of Autonomous Vehicles
Despite their potential benefits, autonomous vehicles also face several challenges before they can become a widespread reality. Some of the main challenges of autonomous vehicles are:
- Technical challenges: Developing reliable and robust autonomous vehicle technology is a complex task requiring advances in artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and control systems. There are also challenges related to ensuring the safety and security of autonomous vehicles and developing effective communication systems for vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure interactions.
- Legal and regulatory challenges: Deploying autonomous vehicles will require new legal and regulatory frameworks that address liability, cybersecurity, and data privacy issues. Developing these frameworks is a complex and time-consuming process involving multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, industry players, and consumer advocates.
- Public acceptance: Autonomous vehicles are a relatively new and unfamiliar technology, and there are concerns among the public regarding their safety, reliability, and impact on employment. Building trust and acceptance among the public is critical for the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
- Infrastructure challenges: Autonomous vehicles require a supportive infrastructure that includes high-speed communication networks, intelligent transportation systems, and charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. Developing this infrastructure requires significant investments and collaboration among multiple stakeholders.
The development and deployment of autonomous vehicles face significant technical, legal, regulatory, public acceptance, and infrastructure challenges. Addressing these challenges will require collaboration among multiple stakeholders and a long-term commitment to research, development, and deployment.
Current State of Autonomous Vehicle Technology
Autonomous vehicle technology has made significant strides in recent years, with many companies investing heavily in research and development. However, the technology is still in its early stages, and several technical and regulatory challenges must be overcome before fully autonomous vehicles become a reality. Currently, most autonomous vehicles are at the Level 2 or Level 3 stage, requiring some human input and supervision. However, some fully autonomous vehicles are tested in controlled environments such as closed campuses or limited geographic areas.
In terms of technology, autonomous vehicles rely on sensors, cameras, and software to perceive their environment and make decisions. However, these technologies still need improvements to ensure greater reliability and safety. There is still a long way to go before fully autonomous vehicles become a common sight on our road.
Future of Autonomous Vehicle Technology
The future of autonomous vehicle technology is promising. Many experts predicting that it will revolutionize how we travel and transport goods. As technology continues to advance, autonomous vehicles are becoming safer, more efficient, and more accessible to the general public. One of the most exciting possibilities of autonomous vehicle technology is the potential to reduce accidents caused by human error. It accounts for the vast majority of road accidents. Additionally, autonomous vehicles could reduce congestion, improve fuel efficiency, and make transportation more affordable. However, many challenges are still present before fully autonomous vehicles become a reality. These include regulatory and legal issues, cybersecurity concerns, and technical challenges. The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles will have significant impacts on industries such as public transportation, logistics, and automotive manufacturing.

The future of autonomous vehicle technology is promising. We can also expect that it will have far-reaching impacts on society and the economy in the coming decades.
Tagged
Share This Article
An Autonomous vehicle uses advanced sensors, cameras, mapping technology, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to navigate roads and operates without human intervention. This article explains the six levels of automation in autonomous vehicles, with Level 0 requiring the driver to perform all tasks and Level 5 operating without human input. It also explains that autonomous vehicles are expected to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and provide accessibility for people with disabilities, challenges remain, including legal and regulatory issues, cybersecurity concerns, and public acceptance. We will also see how ongoing advancements in sensor technology, machine learning, and communication systems will continue to shape the development of autonomous vehicle technology.

What is an Autonomous Vehicle?
An autonomous vehicle, also known as a self-driving car, is a vehicle that can navigate and operate on the road without the need for human intervention. These vehicles are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to perceive their surroundings and respond to traffic conditions in real-time. The combination of these technologies, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms allows autonomous vehicles to make complex decisions and control the vehicle’s movements.
Autonomous vehicles are classified into six levels of automation, ranging from no automation (Level 0) to full automation (Level 5). Level 0 vehicles require the driver to perform all driving tasks, while Level 5 vehicles can operate in any driving condition without human input. The development of autonomous vehicles is set to revolutionize the transportation industry by improving safety, reducing traffic congestion, and providing greater accessibility to transportation for people with disabilities or limited mobility.
However, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles faces several challenges, including legal and regulatory issues, cybersecurity concerns, and public acceptance and trust. Despite these challenges, many companies are investing heavily in developing and testing autonomous vehicle technology, and the future of transportation looks increasingly autonomous.
The Technology Behind Autonomous Vehicle
The technology behind autonomous vehicles is complex and involves a combination of advanced sensors, cameras, mapping, and communication technology. These vehicles use a variety of sensors such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and cameras to perceive their surroundings and collect data about the road, traffic, and other objects. LiDAR sensors use laser light to create a detailed 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings, while radar sensors use radio waves to detect objects and determine their distance and speed.

In addition to sensing technology, autonomous vehicles rely on mapping and localization technology to determine their precise location and route plans. This involves using high-precision GPS and machine-learning algorithms that analyze data from various sensors and sources to create a detailed map of the environment.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also critical components of autonomous vehicle technology, allowing the vehicle to interpret sensor data and decide how to respond to traffic and other objects on the road. Communication technology enables autonomous vehicles to communicate with each other and other infrastructure, such as traffic lights and road signs.
The technology behind autonomous vehicles is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements in areas such as sensor technology, machine learning, and communication systems, paving the way for a future where self-driving cars will be commonplace transportation.
Levels of Autonomous Vehicle
Autonomous vehicles are classified into several levels of automation, each with increasing levels of autonomy. These levels indicate the extent to which the vehicle can operate without human intervention, with the highest level allowing for fully automated driving.

Level 0: No Automation
Level 0 is the lowest level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the driver is solely responsible for all driving tasks. In Level 0 vehicles, there are no automated driving features, and the driver must constantly monitor the road, control the vehicle’s speed, and make decisions regarding acceleration and braking. This level of automation is present in traditional vehicles without advanced driver assistance systems. While Level 0 vehicles do not have any automated features, they may still incorporate safety features such as anti-lock brakes and electronic stability control. However, Level 0 vehicles have some limitations to enhance safety and reduce the workload of the driver, as they require constant manual input and attention from the driver.
Level 1: Driver Assistance
Level 1 is the first level of automation in autonomous vehicles. These vehicles feature basic driver assistance systems. In Level 1 vehicles, the driver controls the steering, acceleration, and braking, but the vehicle can assist in these tasks. Common examples of Level 1 features include adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automated emergency braking. These features use sensors and cameras to detect other vehicles and objects on the road and can provide warnings or intervene to prevent collisions. While Level 1 vehicles provide some assistance to the driver, they still require constant monitoring and control by the driver.
Level 2: Partial Automation
Level 2 is the second level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle can provide more advanced assistance to the driver. In Level 2 vehicles, the vehicle can control both steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver must still remain vigilant and be ready to take control at any time.

Common examples of Level 2 features include Tesla’s Autopilot and General Motor’s Super Cruise, which use a combination of sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to provide advanced driver assistance features such as lane keeping, automated lane changing, and self-parking. However, the driver must still be aware of their surroundings and ready to take over control if necessary. These vehicles represent a significant step towards fully autonomous vehicles, but there are still limitations to the level of autonomy without full control by the vehicle.
Level 3: Conditional Automation
Level 3 is the third level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle is capable of taking full control under certain conditions. In Level 3 vehicles, the driver can relinquish control of the vehicle and allow it to operate autonomously in specific situations, such as on the highway or in traffic jams. However, the driver must still be prepared to take control when prompted by the vehicle.
Level 3 vehicles use advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to perceive their surroundings and decide how to navigate the road. These vehicles can detect traffic lights, road signs, and other road objects and adjust their speed and direction accordingly. However, the driver must remain alert and ready to take control if the vehicle encounters a situation it cannot handle.
Level 3 vehicles offer a higher level of autonomy than Level 2 vehicles. However, there are still limitations to their capabilities, and the driver must be prepared to take control if necessary. The development of Level 3 vehicles is an important step towards fully autonomous vehicles, but there are still challenges to overcome before this level of automation becomes mainstream.
Level 4: High Automation
Level 4 is the fourth level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle can be fully autonomous in certain conditions and environments. In Level 4 vehicles, the vehicle can operate without human intervention in specific situations, such as on highways or in predefined geofenced areas.
Level 4 vehicles use advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technology to detect and interpret their surroundings and can make decisions about navigating the road without any human input. These vehicles can adjust their speed, direction, and response to traffic signals and road conditions and safely navigate most environments without human intervention.
Level 4 vehicles represent a significant milestone in developing autonomous vehicles, as they offer a high level of autonomy without requiring constant human supervision. However, there are still limitations to their capabilities, and the driver may need to take control in certain situations, such as extreme weather conditions or unexpected obstacles on the road. These vehicles significantly improve safety and convenience over traditional vehicles and are a major step towards fully autonomous vehicles.
Level 5: Full Automation
Level 5 is the highest level of automation in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle can be fully autonomous in all conditions and environments without requiring human intervention. In Level 5 vehicles, the driver is completely free from the driving task. The vehicle can operate independently in any situation, including extreme weather conditions and unexpected obstacles on the road.

Level 5 vehicles use a combination of advanced sensors, cameras, mapping technology, and artificial intelligence to perceive their surroundings and make decisions about how to navigate the road. These vehicles can adjust their speed, direction, and response to traffic signals and road conditions and safely navigate any environment without human input.
Full automation offers a significant improvement in safety, efficiency, and convenience over traditional vehicles and has the potential to transform transportation as we know it. However, the development and deployment of Level 5 vehicles are still in the early stages. Significant technical, legal, and societal challenges are present before they become a reality.
Applications of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles have a wide range of potential applications across different industries and sectors. Some of the most promising applications of autonomous vehicles include:
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles can provide an efficient and safe mode of transportation for people and goods. They can be used for public transportation, ride-sharing, delivery services, and more.
- Logistics and supply chain: Autonomous vehicles can improve the efficiency and accuracy of logistics and supply chain operations by automating the movement of goods and reducing the need for manual labor.
- Agriculture: Autonomous vehicles can be used in agriculture to automate tasks such as planting, watering, and harvesting crops, improving efficiency and reducing the need for manual labor.
- Mining: Autonomous vehicles can be used in mining operations to automate the movement of materials and reduce the risk of accidents in hazardous environments.
- Construction: Autonomous vehicles can be used in construction to automate tasks such as excavation, demolition, and transportation of materials, improving safety and efficiency.
- Military: Autonomous vehicles can be used in military operations to support reconnaissance, surveillance, and logistics, reducing the risk to human personnel.
- Emergency services: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to use in emergency services to transport people and supplies to disaster areas or provide remote medical assistance.

Autonomous vehicles have the potential to revolutionize various industries and improve safety, efficiency, and sustainability. However, their widespread adoption depends on overcoming technical, legal, and societal challenges, such as ensuring safety, addressing ethical concerns, and integrating them with existing infrastructure and systems.
Advantages of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles have numerous advantages over traditional vehicles, which make them an attractive technology for future transportation systems. Some of the main advantages of autonomous vehicles are:
- Increased safety: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to greatly reduce the number of accidents caused by human error, which is estimated to be the cause of over 90% of all accidents. By using advanced sensors and algorithms, autonomous vehicles can detect and avoid obstacles and hazards in the environment. It makes them safer than human-driven vehicles.
- Improved traffic flow: Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other and the surrounding infrastructure to optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and travel times.
- Increased efficiency: Autonomous vehicles can operate more efficiently than human-driven vehicles by reducing unnecessary acceleration and braking and optimizing routes based on real-time traffic conditions.
- Improved accessibility: Autonomous vehicles can provide greater mobility for people who are unable to drive, such as the elderly and disabled, improving their independence and quality of life.
- Reduced environmental impact: Autonomous vehicles can be designed to operate on electric power, reducing their emissions and contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
- Lower operating costs: Autonomous vehicles can reduce the cost of transportation by reducing the need for human drivers and optimizing maintenance schedules.
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to improve safety, efficiency, accessibility, and sustainability in transportation. However, their widespread adoption will require significant investments in research and development, infrastructure, and public acceptance.
Challenges of Autonomous Vehicles
Despite their potential benefits, autonomous vehicles also face several challenges before they can become a widespread reality. Some of the main challenges of autonomous vehicles are:
- Technical challenges: Developing reliable and robust autonomous vehicle technology is a complex task requiring advances in artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and control systems. There are also challenges related to ensuring the safety and security of autonomous vehicles and developing effective communication systems for vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure interactions.
- Legal and regulatory challenges: Deploying autonomous vehicles will require new legal and regulatory frameworks that address liability, cybersecurity, and data privacy issues. Developing these frameworks is a complex and time-consuming process involving multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, industry players, and consumer advocates.
- Public acceptance: Autonomous vehicles are a relatively new and unfamiliar technology, and there are concerns among the public regarding their safety, reliability, and impact on employment. Building trust and acceptance among the public is critical for the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
- Infrastructure challenges: Autonomous vehicles require a supportive infrastructure that includes high-speed communication networks, intelligent transportation systems, and charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. Developing this infrastructure requires significant investments and collaboration among multiple stakeholders.

The development and deployment of autonomous vehicles face significant technical, legal, regulatory, public acceptance, and infrastructure challenges. Addressing these challenges will require collaboration among multiple stakeholders and a long-term commitment to research, development, and deployment.
Current State of Autonomous Vehicle Technology
Autonomous vehicle technology has made significant strides in recent years, with many companies investing heavily in research and development. However, the technology is still in its early stages, and several technical and regulatory challenges must be overcome before fully autonomous vehicles become a reality. Currently, most autonomous vehicles are at the Level 2 or Level 3 stage, requiring some human input and supervision. However, some fully autonomous vehicles are tested in controlled environments such as closed campuses or limited geographic areas.
In terms of technology, autonomous vehicles rely on sensors, cameras, and software to perceive their environment and make decisions. However, these technologies still need improvements to ensure greater reliability and safety. There is still a long way to go before fully autonomous vehicles become a common sight on our road.
Future of Autonomous Vehicle Technology
The future of autonomous vehicle technology is promising. Many experts predicting that it will revolutionize how we travel and transport goods. As technology continues to advance, autonomous vehicles are becoming safer, more efficient, and more accessible to the general public. One of the most exciting possibilities of autonomous vehicle technology is the potential to reduce accidents caused by human error. It accounts for the vast majority of road accidents. Additionally, autonomous vehicles could reduce congestion, improve fuel efficiency, and make transportation more affordable. However, many challenges are still present before fully autonomous vehicles become a reality. These include regulatory and legal issues, cybersecurity concerns, and technical challenges. The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles will have significant impacts on industries such as public transportation, logistics, and automotive manufacturing.

The future of autonomous vehicle technology is promising. We can also expect that it will have far-reaching impacts on society and the economy in the coming decades.




![How To Fake GPS Location on iPhone Without Jailbreaking [2023]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwriteflow-media.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fsites%2F16%2Fmedia%2F2025%2F10%2Fgps-location-feature-wlaR2F.webp&w=3840&q=75)